Tomographic ultrasound image Typical Bochdalec hernia is seen Tomographic image clearly shows oppressed and hypoplastic left lung, heart replacement to the right, and the stomach inside thoracic space Fig 35 Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM) at 24 weeks (Left) Tomographic ultrasound sagittal image of fetal chestIf you have an ultrasound done late in your pregnancy, your doctor may notice it then Treatment Your doctor will begin to correct your baby's clubfoot shortly after they're bornAbout 25% of affected fetuses are stillborn and about 30% die in the neonatal period The birth prevalences of the most common dysplasias are shown in the Table on the next page
2
Club foot ultrasound images
Club foot ultrasound images-Abstract Five cases of congenital clubfoot diagnosed prenatally by ultrasound are reported The incidence of clubfoot may be higher within an affected family and may be associated with other structural anomalies or chromosomal abnormalities Identifying a clubfoot in utero should therefore alert the sonographer that other anomalies may beThis board will feature pins about any and all about clubfoot See more ideas about club foot, club foot baby, expecting baby




The Clubfoot Chronicles The Saga Begins
Ultrasound and sagittal T2 images of the superior limb reduction The malformations observed were "Strawberry" calvarium cerebellar hypoplasia ventricular septal defect and overriding aorta liver herniation with normal insertion of the umbilical cord in the abdomen superior limb reduction left club foot intrauterine growth restriction The diagnosis was changed after followup ultrasound scan in 13 fetuses (25%), and the final ultrasound diagnosis was normal in one fetus, isolated club foot in 31 fetuses, and complex club foot in fetuses At birth, club foot was found in 79 feet in 43 infants for a positive predictive value of %And (2) determine whether various ultrasound (US) variables correlated with each other and with the Pirani score before and after treatment Methods We prospectively followed 17 infants (25 clubfeet) assessed using the Pirani score and US variables (medial malleolus navicular distance, navicular alignment in relation to the talar head,
Abstract In this chapter, we review the diagnosis and underlying potential causes for isolated clubfoot (Talipes Equinovarus) Prenatal ultrasound (US) findings in particular are described, along with accompanying images to augment the reader's understanding Doctors use a number of different imaging procedures to look at the structures within our feet and ankles One of the most commonly used of these procedures is foot and ankle ultrasound (also known as a sonogram), which uses highfrequency sound waves to form an image of the bones and other parts of the foot and ankleThis technique has been around for over fifty The first two pictures show curved foot However I have bunch of images that show perfectly straight feet/legs From my research the Clubfoot is fixed and supposed to stay in that position Dr wrote in her report "right foot clubbed Not consistent through ultrasound" We opted for amnio, which was normal (I am 41)
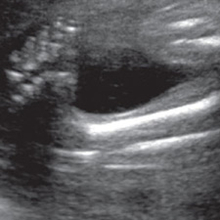
Image Gallery Click each image to enlarge Fetal nose/lips Fetal nose, upper and lower lip The arrow is pointing to the tip of the nose 1st trimester (Expecting a baby who will be born with clubfoot?This results in the dorsum of the foot being rotated medially with the ultrasound images showing the metatarsals and phalanges of the affected foot in the same view and same plane as the tibia and fibula of the lower leg This also results in the foot having a club like appearance and is called club foot or congenital talipes equinovarus



2



When Your Baby Has Clubfoot Answers For Expecting Parents Boston Children S Answers
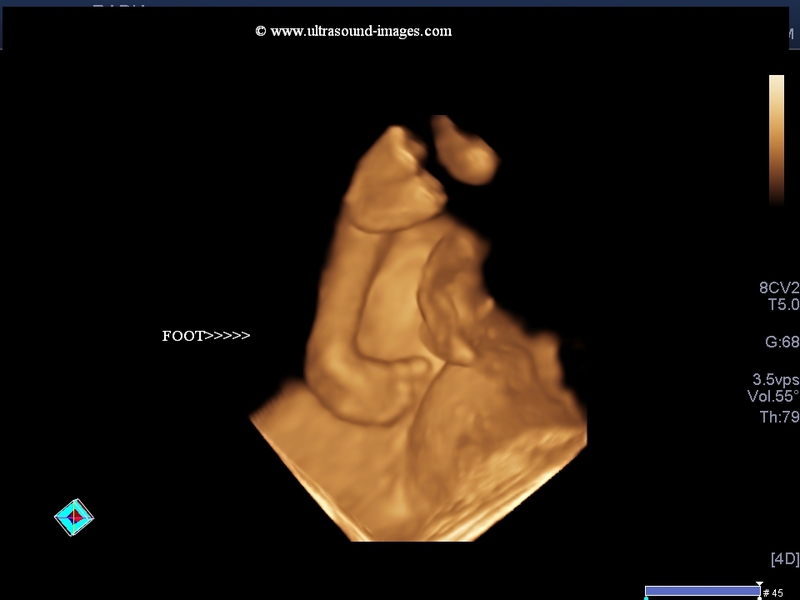
Ultrasound Case 9 Ultrasound Images of an interdigital neuroma The Ankle, Foot and Orthotic Centre's Northcote Podiatrists can help you with all lower limb complaints, including Interdigital Neuromas Make an appointment to get your foot and ankle pain under controlIn this case of isolated unilateral clubfoot at 24 weeks, 3D ultrasound shows a right clubfoot and a normal left foot 3D images allow for better appreciation of the severity of the clubfoot 3D bonerendered views allows for visualization of the tibia , fibula , and metatarsals Being able to count metatarsals and toes is important forCommittee approved the study protocol (MEC As the diagnosis of a congenital clubfoot is based 04–227 – , combining METC on the subjective assessment of the ultrasound /03/177, METC /03/178, MEC images, there is, especially at the end of the first tri 04–227) mester, a need for a measurement tool




The Clubfoot Chronicles The Saga Begins




Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis Of Club Foot The Bone Joint Journal
15,074 Club Foot Premium High Res Photos Browse 15,074 club foot stock photos and images available, or search for clubfoot to find more great stock photos and pictures sister helping disabled baby brother club foot stock pictures, royaltyfree photos & images club foot club foot stock illustrations there are several things that can cause club foot like position, t18, and ehlersdanlos syndrome or it could be just a bad ultrasound image get information and make a plan remember how precious your little one is and work through it togetherMRI imaging for posterior tibial tendinopathy can be taken with T1 and T2 weighted images Contrast can also be used to enhance the image The foot is typically held in a neutral position and sagittal and axial images are taken of the tendon Color sonography can also been used to detect posterior tibial tendinopathy




Clubfoot Versus Positional Foot Deformities On Prenatal Ultrasound Imaging Brasseur Daudruy Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library



Ssrd Interesting Cases Fetal Clubfoot Ultrasound Image 3d Image
Club foot present as an inturn of one foot or both feet Diagnosis The condition can be diagnosed inutero via ultrasound or at birth Visual identification of club foot is all that is needed for diagnosis Treatment There are two treatments currently used to treat club foot – the Ponseti Method and surgery Clubfoot is frequently found during the anatomy ultrasound (around weeks of pregnancy) when your doctor will be looking at your baby's anatomy in detail Most of the time, clubfoot is isolated However, your doctors will look carefully for any additional signs that may be suggestive of an underlying condition (such as a chromosome condition ) Fig 51 Images obtained with 3D ultrasound in which the surface renderization enables us to obtain coronal, oblique, and sagittal planes of normal fetuses with gestational ages between 27 and 33 weeks 522 Profile Views In the profile view we study 1 The forehead (elusive or convex) and discard prefrontal edema (Fig 52) Fig 52
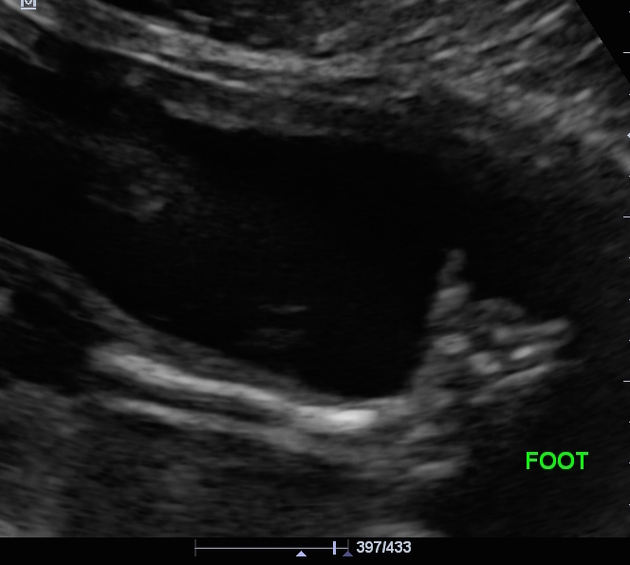



Club Foot Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org



2
Ultrasound of the Foot and AnkleA suspected diagnosis of clubfoot can be determined via prenatal ultrasound as early as 13 weeks, but it is typically discovered during an ultrasound around weeks gestation The severity of the clubfoot often cannot be determined until after delivery Around 10% of babies with clubfoot have another fetal conditionUltrasound Case 3 Ultrasound Images of midportion of the Achilles tendon with deep soleal fibre irritation The Ankle, Foot and Orthotic Centre's Northcote Podiatrists can help you with all lower limb complaints, including Achilles tendinopathy Make an appointment to get your foot and ankle pain under control




Clubfoot Orthopaedia



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus
Ultrasound images 62,939 ultrasound stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See ultrasound stock video clips of 630 ultrasonography pregnant ultrasound ultrasonography woman thyroid pregnancy male ultrasound pregnant woman having ultrasound ultrasound image thyroid and pregnancy ultrasound table ultrasound breast Clubfoot can be identified in the first or second trimester Threedimensional or fourdimensional US is useful in the evaluation of fetuses with skeletal abnormalities, especially for imaging of the extremities (Figs 643 and 644) Download Download fullsize image;Clubfoot 3D Ultrasound (rendering mode) Download a 190K clip of club foot SKELETAL ANOMALIES Prevalence Skeletal dysplasia is found in about 1 per 4000 births;
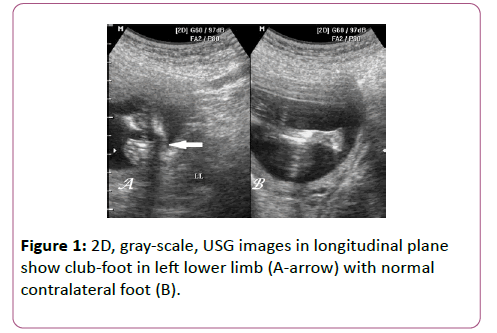



Antenatal 3d Usg In Unilateral Club Foot A Rare Anomaly Insight Medical Publishing




Skeleton Diagnosis Of Fetal Abnormalities The 18 23 Weeks Scan
Ility of the Ponseti method in correcting clubfeet; INTRODUCTION Clubfoot, or talipes equinovarus, refers to a developmental deformity of the foot in which one or both feet are excessively plantar flexed, with the forefoot swung medially and the sole facing inward ()It is a common congenital malformation, typically discovered at the time of birth as an isolated anomaly in an otherwise normal neonate Clubfoot, or talipes equinovarus, is a congenital deformity consisting of hindfoot equinus, hindfoot varus, and forefoot varusThe deformity was described as early as the time of Hippocrates The term talipes is derived from a contraction of the Latin words for ankle, talus, and foot, pesThe term refers to the gait of severely affected patients, who walked on their ankles
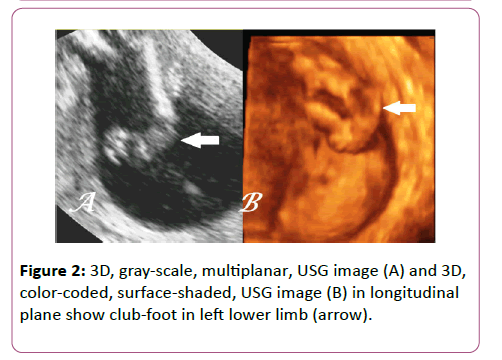



Antenatal 3d Usg In Unilateral Club Foot A Rare Anomaly Insight Medical Publishing




3 D Ultrasound Of Club Foot
Visit http//wwwsonositecom/education/An overview of a scanning technique for a foot exam including probe type, probe position, ultrasound settings, and kUltrasound images are displayed in either 2D, 3D, or 4D (which is 3D in motion) The ultrasound probe (transducer) is placed over the carotid artery (top) A color ultrasound image (bottom, left) shows blood flow (the red color in the image) in the carotid artery Waveform image (bottom right) shows the sound of flowing blood in the carotid artery Clubfoot was diagnosed in 037% (150) prenatal ultrasound anomaly scans Following exclusion for missing information, 109 fetuses remained for analysis Bilateral and unilateral clubfoot were diagnosed in 467% and 532%, respectively Isolated presentation in 697% and complex in 302% 44% of fetuses underwent invasive diagnostic testing



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus



Club Foot
An ultrasound scan in Glendale CA is a diagnostic tool that uses imaging to view internal organs It can also be used to assess blood flow through the vessels in the body Ultrasounds are highly useful for pregnant women to check on the developing baby and it works by using highfrequency sound waves I have heard some babies look like having club foot on ultrasound and perfectly normal when born I know we wont know anything for sure until further diagnosis but just looking for some positive experiences #1 Bluenpinkmom, Christie11 WellKnown Member Joined Messages Introduction Conventional radiography has been used for many years to assess clubfoot In the infant, its value is limited because major parts of the studied bones have not yet ossified Although the techniques are still evolving, US was used in many studies to assess clubfoot 3–6, 11, 13, 18, , 26, 27, 32, 34US allows observation of the cartilaginous




Pdf Clinical Outcome Of Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Diagnosed Antenatally By Ultrasound Semantic Scholar




Clubfoot Versus Positional Foot Deformities On Prenatal Ultrasound Imaging Brasseur Daudruy Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
The Clubfoot Chronicles Our clubfoot journey began on , when I was 19w3d pregnant with our fifth child I went to my OB/GYN's office for my routine week anatomy ultrasound, along with my husband and my two oldest children (We did not find out his/her gender, and refer to the baby as "Tiebreaker," since s/he has two brothers andOBJECTIVE The purpose of this article is to review the appropriate use of ultrasound in the workup of softtissue masses of the extremities The normal sonographic appearance of superficial soft tissues, the importance of proper technique in image acquisition, and the characteristic sonographic appearance of certain masses and potential pitfalls are discussed A number of studies have investigated the FPR of isolated clubfoot on ultrasound either based on the number of fetuses or based on the number of feet that are normal or have positional deformities postnatally over the total group of prenatally diagnosed cases or feet The FPRs vary greatly between studies with values of 0% 13,




Prenatal Detection Of Clubfoot Key Points The Obg Project




Amazing Results In Clubfoot Treatment For Young Riwan Steps
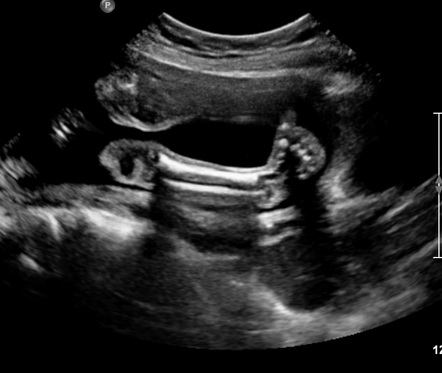
Fig 641 Clubfoot (arrow) in a 12week fetusEFETAL CLUB FOOT F FETAL FOOT These are ultrasound images of a 2nd trimester fetus, which show a neural tube defect (spina bifida) of the lower lumbar vertebrae There is also splaying of the vertebral laminae and widening of the interpedicular distance in this regionFive cases of congenital clubfoot diagnosed prenatally by ultrasound are reported The incidence of clubfoot may be higher within an affected family and may be associated with other structural anomalies or chromosomal abnormalities Identifying a clubfoot in utero should therefore alert the sonographer that other anomalies may be present and should lead to a detailed structural survey




Talipes Equinovarus Deformity Detected On Ultrasound Examination On 14 Download Scientific Diagram



Club Foot
The diagnosis was changed after followup ultrasound scan in 13 fetuses (25%), and the final ultrasound diagnosis was normal in one fetus, isolated club foot inClub foot is a relatively common finding during antenatal scan Imaging the entire foot in the same plane as tibia/fibula is recognized as a simple hallmark in imaging for might be dealing with a club foot kimmyt09 member May 12 in 3rd Trimester I just left my 27 week OB appt where he (finally) went over my week scan Apparently one of the baby's feet was looking "off" and the tech marked some concern for a club foot My dr said more often then not it turns out to be nothing, and even if he does end up




Reviews Chews How Tos Penelope S Clubfoot Journey So Far



Tackling Talipes Early With A Team Approach Children S Hospital Of Philadelphia
A clubfoot, or talipes equinovarus 1 (TEV), is a birth defect The foot is twisted in (inverted) and down Without treatment, persons afflicted often appear to walk on their ankles, or on the sides of their feet It is a common birth defect, occurring in about one in every 1,000 live births Foot Ultrasound KEY FACTS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS • Common specific indications Suspected plantar fasciitis and fibroma, Morton neuroma, ganglia, osteoarthritis, gout, and other joint disorder



A Gallery Of High Resolution Ultrasound Color Doppler 3d Images Fetal Face And Neck




Value Of The Fetal Plantar Shape In Prenatal Diagnosis Of Talipes Equinovarus Liao 12 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library




Ultrasound Two And Three Dimensional Images Of Clubfoot At 18 Weeks Of Download Scientific Diagram




Clubfoot Versus Positional Foot Deformities On Prenatal Ultrasound Imaging Brasseur Daudruy Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library



My Journey With Baby S Positional Clubfoot Part 1 Baby Gizmo



Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Club Foot




The Clubfoot Chronicles The Saga Begins



Club Foot



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus
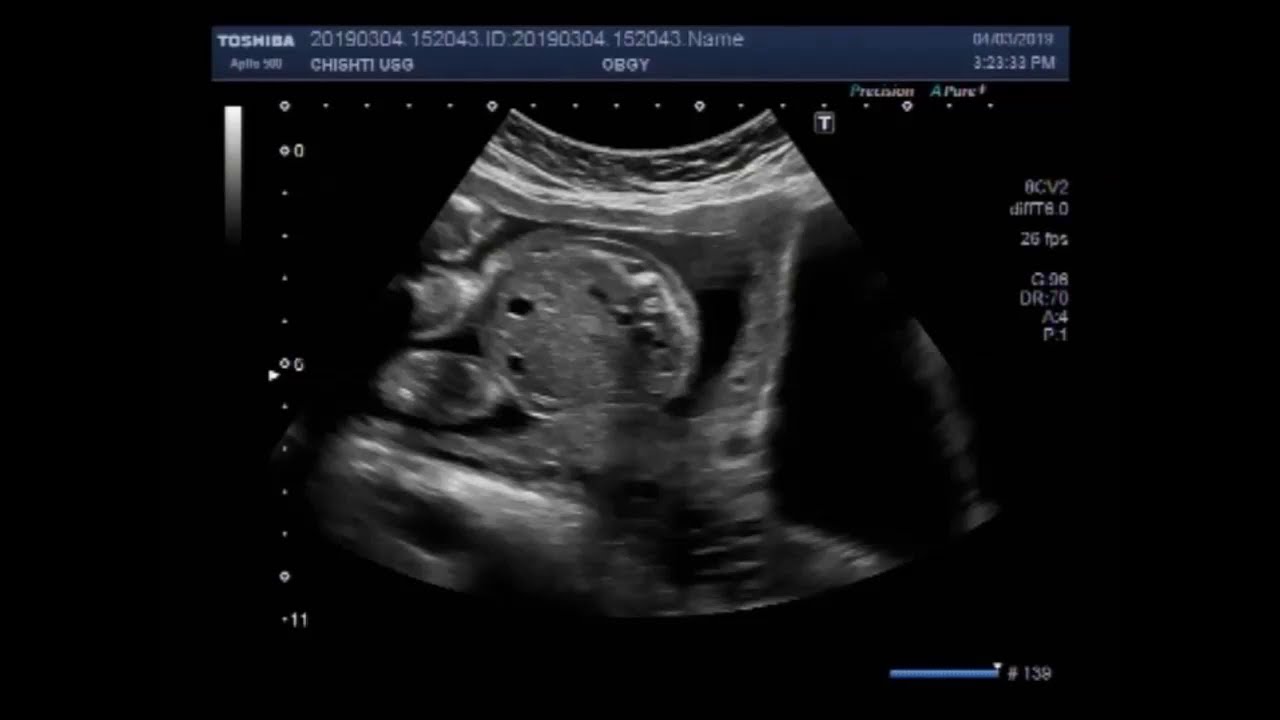



Ultrasound Video Showing Fetal Club Foot And Soft Tissue Edema Youtube



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus




Fetal Clubfoot Ultrasound Services In Ernakulam Ultrascan Centre Id




Pdf Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis Of Club Foot Outcome And Recommendations For Counselling And Follow Up Semantic Scholar




Three Dimensional 3d Ultrasound Studies A Bilateral Club Foot Download Scientific Diagram




The Clubfoot Chronicles The Saga Begins
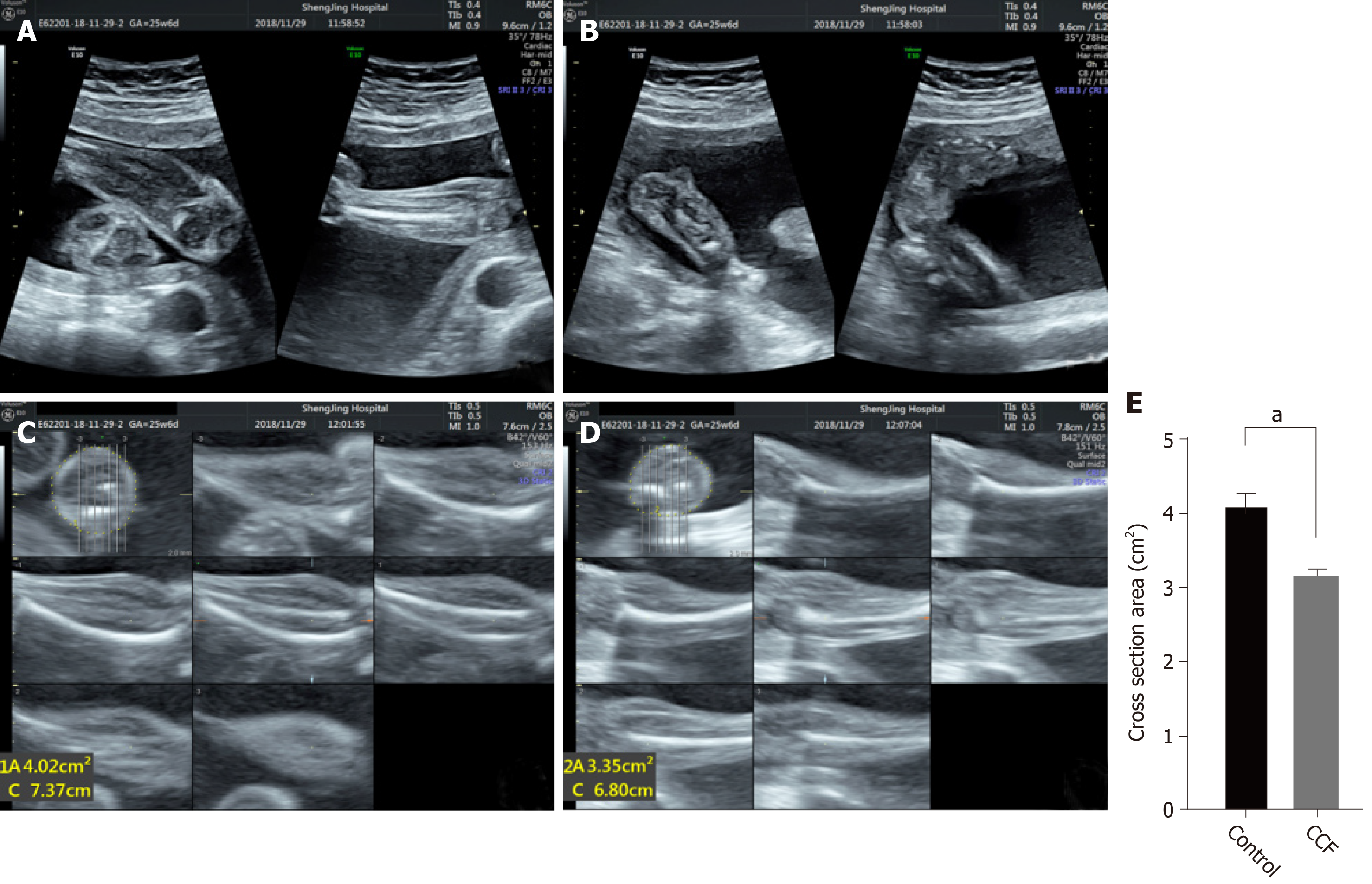



Taz And Myostatin Involved In Muscle Atrophy Of Congenital Neurogenic Clubfoot




The Clubfoot Chronicles The Saga Begins




Clubfoot Treatment Bilateral Club Feet Foot Pain



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus




In Honor Of World Clubfoot Day My Journey As A Clubfoot Mama Katy Moms




Correlations Between Physical And Ultrasound Findings In Congenital Clubfoot At Birth Sciencedirect




Correlations Between Physical And Ultrasound Findings In Congenital Clubfoot At Birth Sciencedirect




The Clubfoot Chronicles The Saga Begins




The Clubfoot Chronicles The Saga Begins



2



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus




Clubfoot




Clubfoot Versus Positional Foot Deformities On Prenatal Ultrasound Imaging Brasseur Daudruy Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library




Prenatal Clubfoot Increases The Risk For Clinically Significant Chromosomal Microarray Results Analysis Of 269 Singleton Pregnancies Sciencedirect




Radiography And Sonography Of Clubfoot A Comparative Study Semantic Scholar




Clubfoot In Children Lurie Children S



1




Just Had Anatomy Scan What Do Y All Think Clubfoot Forums What To Expect




How Parents And The Internet Transformed Clubfoot Treatment Shots Health News Npr




My Journey With Baby S Positional Clubfoot Part 1 Baby Gizmo



Club Foot Talipes Equinovarus Ankle Foot And Orthotic Centre




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Pdf Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis Of Club Foot Outcome And Recommendations For Counselling And Follow Up Semantic Scholar




Clubfoot At 22 Second Weeks Gestation The Forefoot Arrows Is Download Scientific Diagram




The Significance Of Prenatally Identified Isolated Clubfoot Is Amniocentesis Indicated American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology
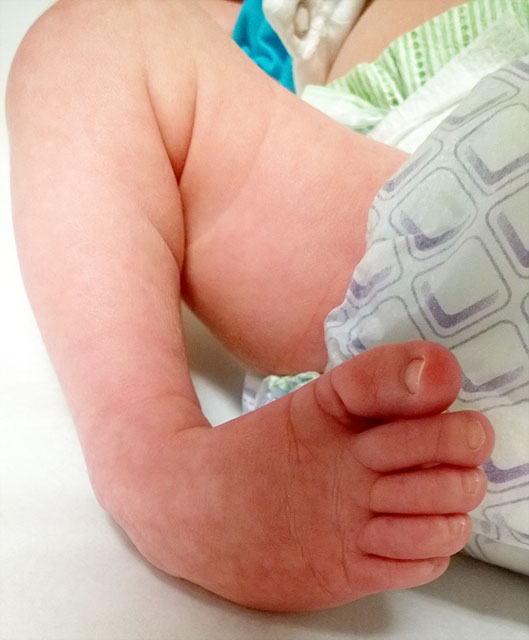



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine
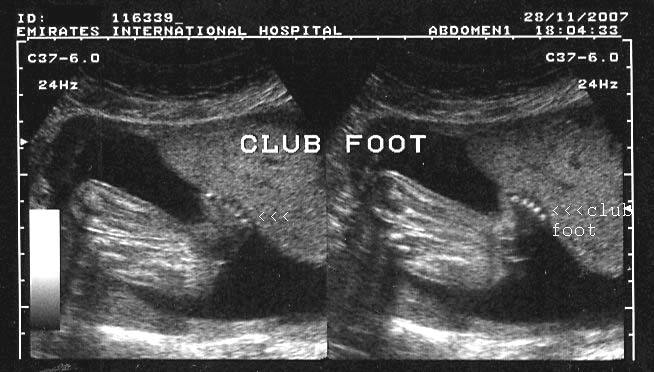



A Gallery Of High Resolution Ultrasound Color Doppler 3d Images Fetal Spine



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus




404 Not Found Ultrasound Sonography Ultrasound Sonography
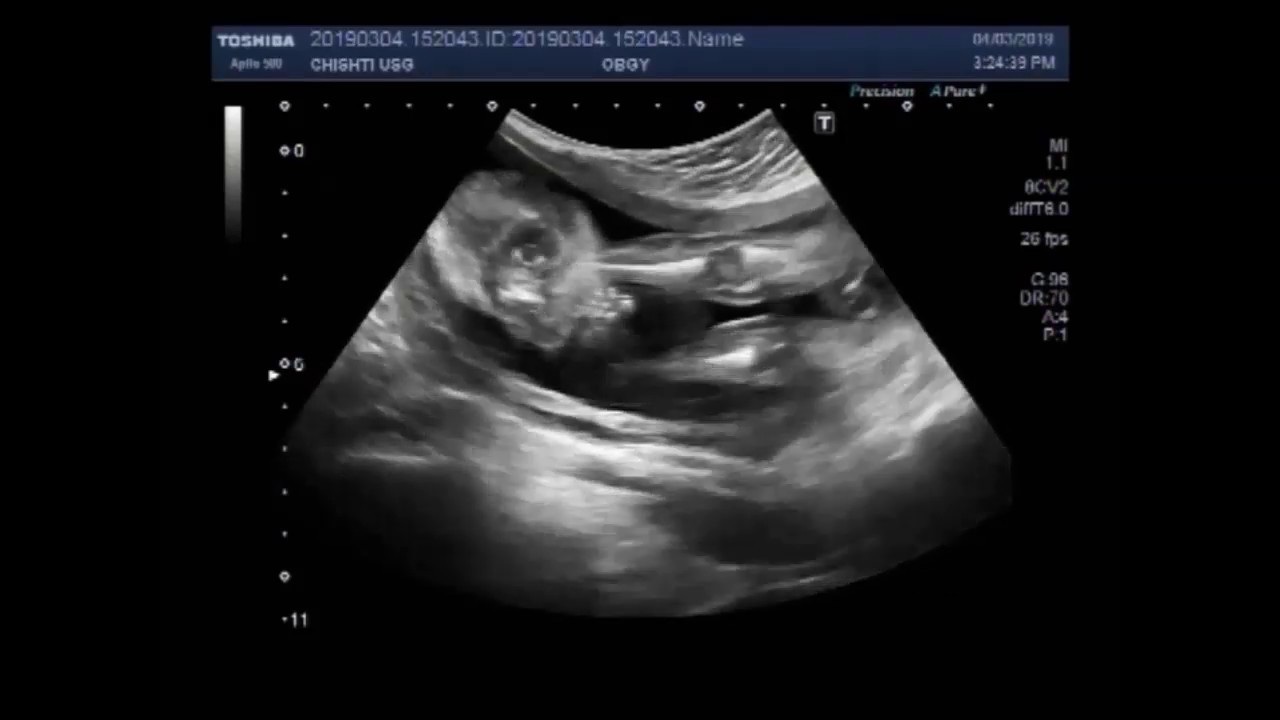



Ultrasound Video Showing Club Foot Fetal Anomaly Scan Youtube




Club Foot Antenatal Ultrasound Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org



Misdiagnosed Clubfoot




My Baby Has A Club Foot Babycenter




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org




1 Sonographers Do It In The Dark Ideas In 21 Diagnostic Medical Sonography Ultrasound Tech Work Humor
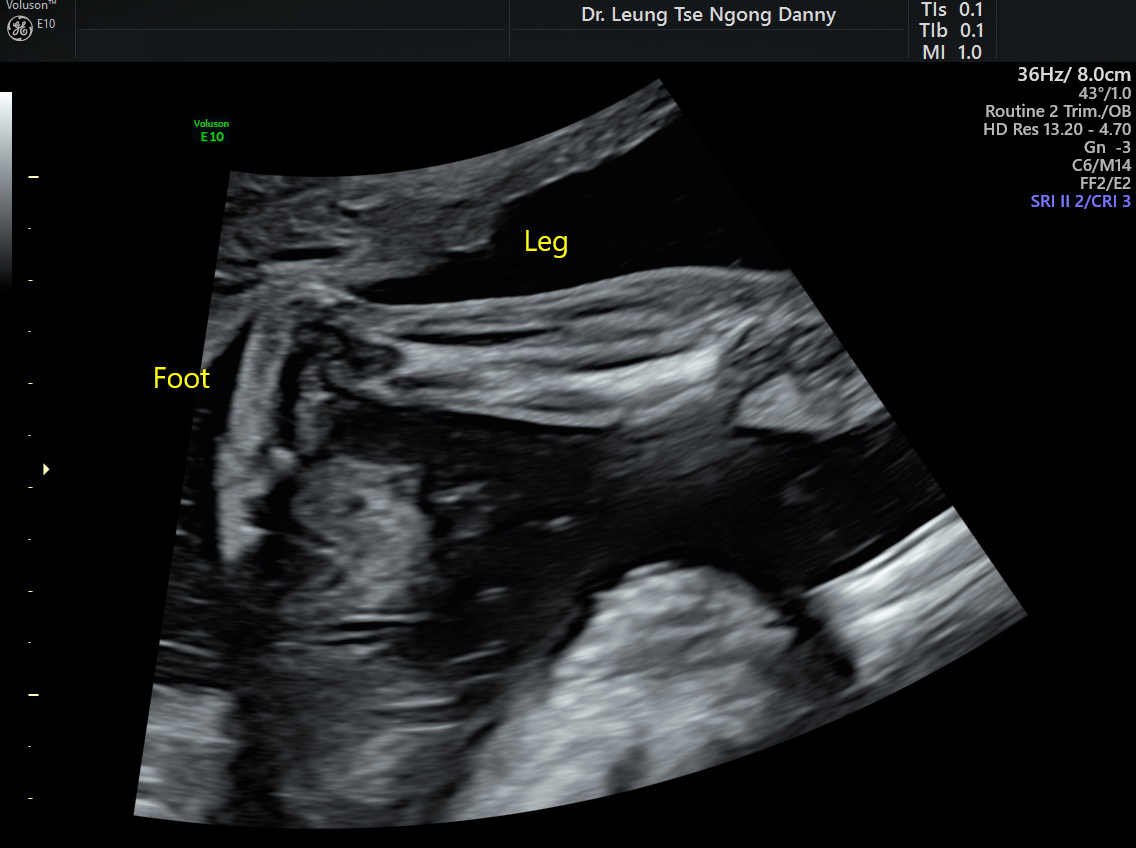



Club Foot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Hkog Info




Skeleton Diagnosis Of Fetal Abnormalities The 18 23 Weeks Scan



Clubfoot Talipes Equinovarus Radiology Key



Club Foot In Ultrasound Babycenter
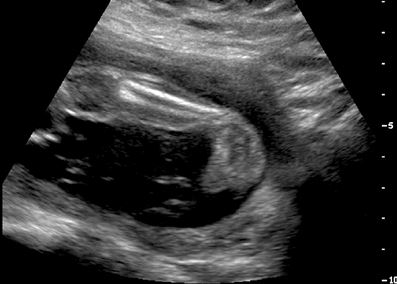



Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets




Pdf Congenital Talipes Equinovarus A Case Report Of Bilateral Clubfoot In Three Homozygous Preterm Infants Semantic Scholar




Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis Of Club Foot The Bone Joint Journal
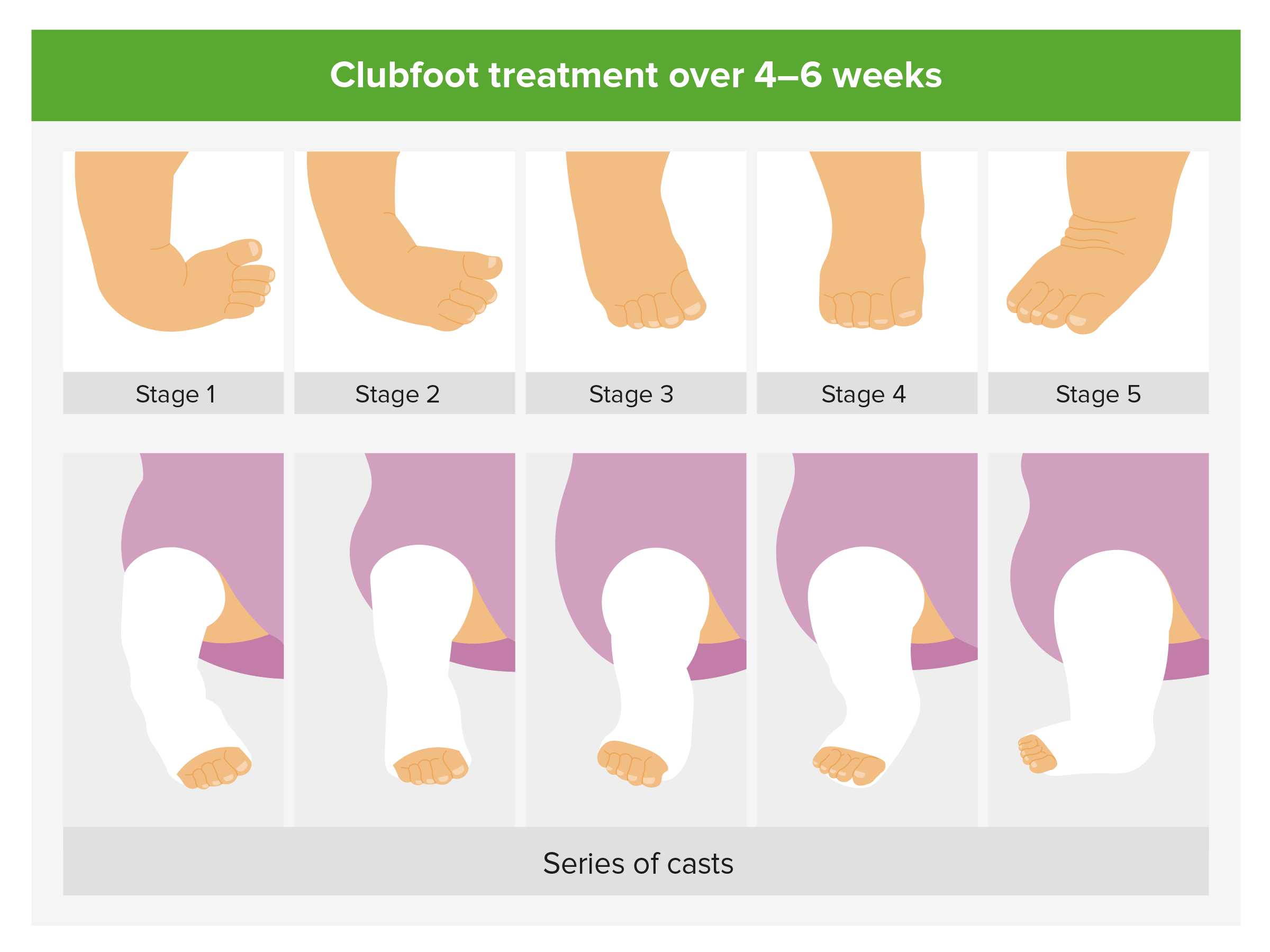



Foot Deformities Concise Medical Knowledge



1
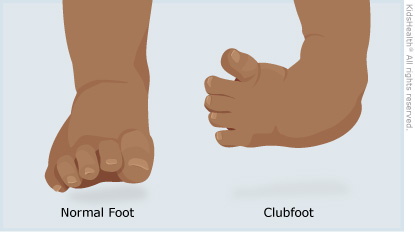



Clubfoot For Parents Nemours Kidshealth




Please Put My Mind At Ease March Babies Forums What To Expect



Ultrasound Video Showing A Case Of Club Foot Also Called Talipes Equinovarus Tev Youtube




Bilateral Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Deformity In Fetus Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org




Pdf Congenital Talipes Equinovarus A Case Report Of Bilateral Clubfoot In Three Homozygous Preterm Infants Semantic Scholar



Tackling Talipes Early With A Team Approach Children S Hospital Of Philadelphia



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus




Clubfoot Versus Positional Foot Deformities On Prenatal Ultrasound Imaging Brasseur Daudruy Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
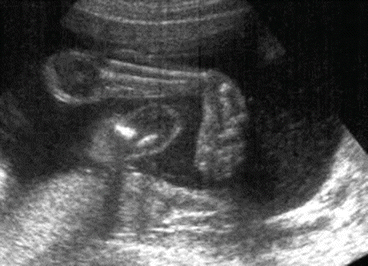



Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot Musculoskeletal Key



Club Foot



1




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital
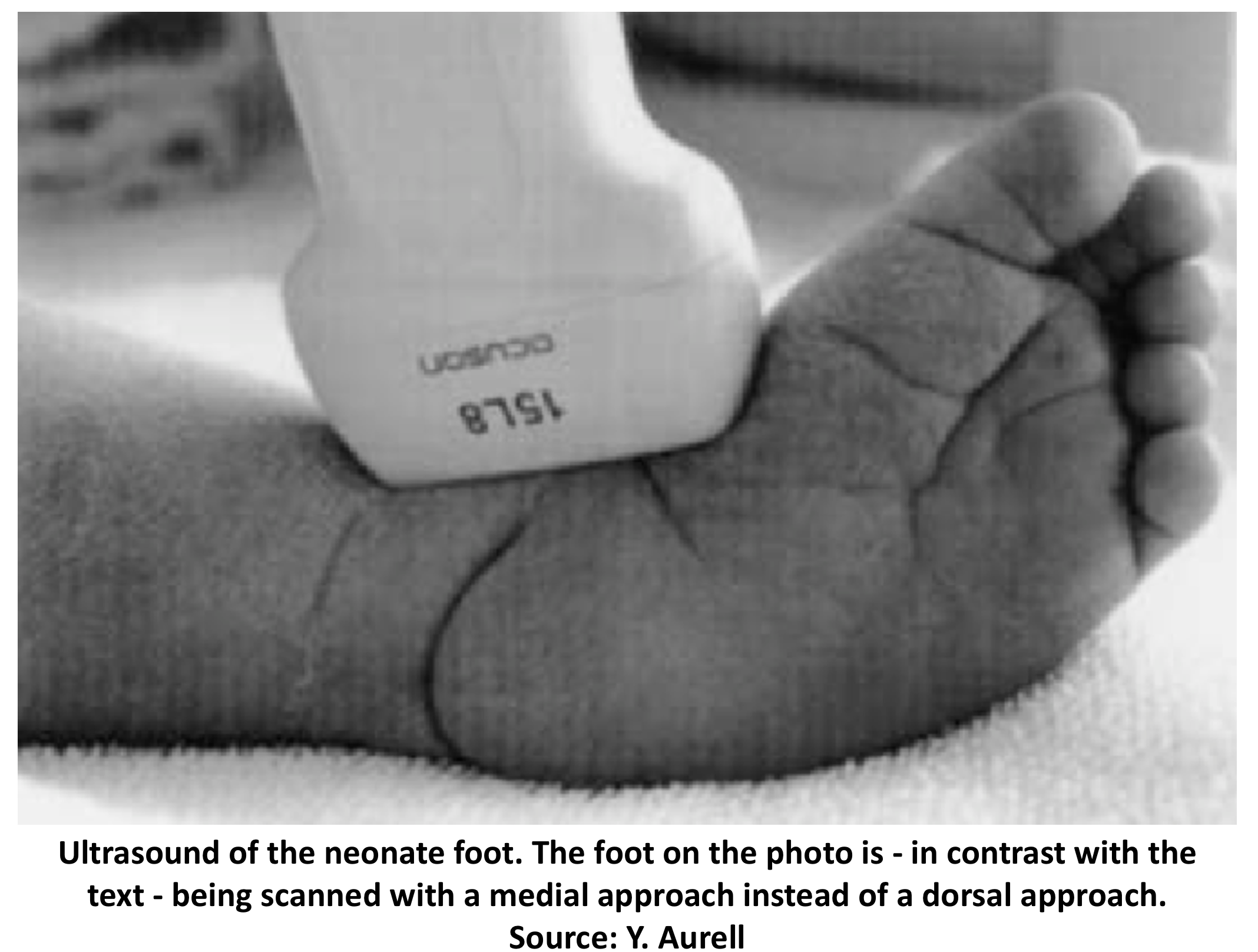



Dynamic Real Time Ultrasound Of The Clubfoot And Ankle Joint Sonoskills




Clubfoot Versus Positional Foot Deformities On Prenatal Ultrasound Imaging Brasseur Daudruy Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus
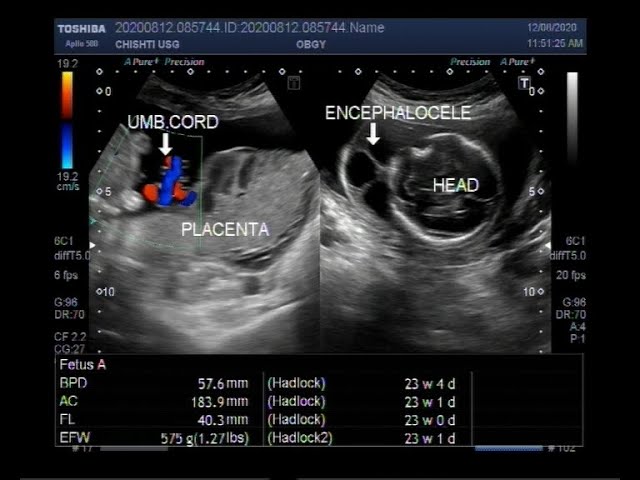



Ultrasound Video Showing Fetal Anomalies Clubfoot Encephalocele Kyphosis And Placental Mass Youtube




Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis Of Club Foot The Bone Joint Journal




Pdf Clinical Outcome Of Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Diagnosed Antenatally By Ultrasound Semantic Scholar



Clubfoot Deformity Talipes Equinovarus




The Ultrasound Images Of Fetus Diagnosed As Clubfoot Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿